In today's era of information explosion, particularly in the field of scientific research, the emergence of fake papers is becoming increasingly difficult to guard against.
Recently, a researcher from Binghamton University in New York, Ahmed Abdeen Hamed, has developed a machine learning algorithm called xFakeSci that can identify forged academic papers with an accuracy rate of up to 94%.
Hamed stated that his main research focus is biomedical informatics, and during the pandemic, fake research articles have been proliferating.
He and his team conducted numerous experiments, creating 50 fake articles on hot medical topics such as Alzheimer's, cancer, and depression, and compared them with real articles on the same subjects. He hopes to discover differences and patterns through this method.
During the research, Hamed extracted relevant literature from the National Institutes of Health's PubMed database and used the same keywords to request ChatGPT to generate papers. His intuition told him that there must be some pattern between fake and real papers.
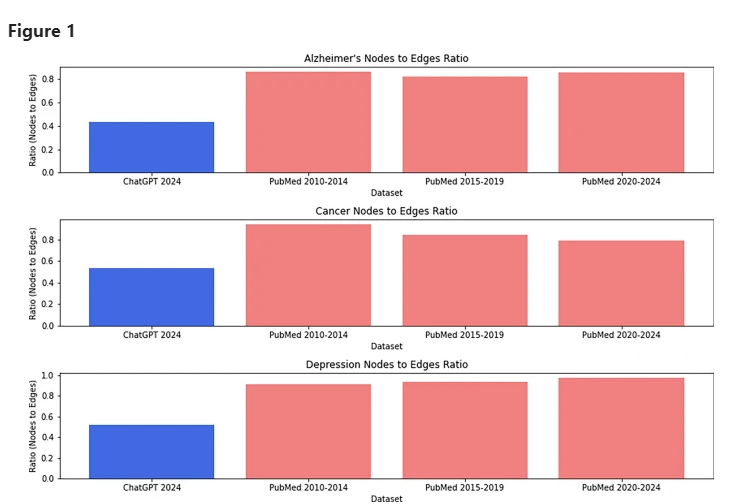
Node and edge ratios of different datasets: ChatGPT versus scientific articles.
After in-depth analysis, the xFakeSci algorithm primarily focuses on two features: one is the bigrams in the articles, such as "climate change" and "clinical trials," and the other is the associations of these bigrams with other words and concepts.
He found that the number of bigrams appearing in fake papers is significantly less than in real ones, although these bigrams are closely connected with other content in fake papers.
He pointed out that AI-generated papers are often intended to convince readers, while the goal of human researchers is to truthfully report experimental results and methods.
In the future, Hamed plans to extend the xFakeSci algorithm to more fields, including engineering, science, and humanities, to verify whether the characteristics of fake papers are consistent. He emphasized that as AI technology continues to advance, the difficulty of identifying true and false papers will increase. Therefore, designing a comprehensive solution is尤为 important.
Although the current algorithm can detect 94% of fake papers, there is still a 6% chance of missing fake literature. He humbly stated that although significant progress has been made, continuous efforts are needed to improve the detection rate and raise public awareness.
Paper entry: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-66784-6
Key points:
📄 **New tool xFakeSci can identify fake research papers with up to 94% accuracy, safeguarding scientific research.**
🧪 **Researchers created numerous fake papers and compared them with real ones, finding significant differences in writing style.**
🔍 **The algorithm will be expanded to more fields in the future to address the increasingly complex challenge of AI-generated papers.**









