Recently, a project named Q* was unveiled by a research team from Kunlun Wanwei's Yan Shuicheng team in China and Nanyang Technological University in Singapore. This project aims to enhance the reasoning capabilities of smaller models. Unlike OpenAI, Q* enables these smaller models to achieve reasoning abilities comparable to models with tens or even hundreds of times more parameters.
The research team has achieved significant results through experiments with the Q* algorithm: on the GSM8K dataset, Q* helped improve the accuracy of Llama-2-7b to 80.8%, surpassing ChatGPT.
On the MATH dataset, Q* helped DeepSeek-Math-7b achieve an accuracy of 55.4%, surpassing Gemini Ultra.
On the MBPP dataset, Q* helped CodeQwen1.5-7b-Chat achieve an accuracy of 77.0%, narrowing the gap with GPT-4's programming level. These results demonstrate the potential of the Q* algorithm in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of smaller models.
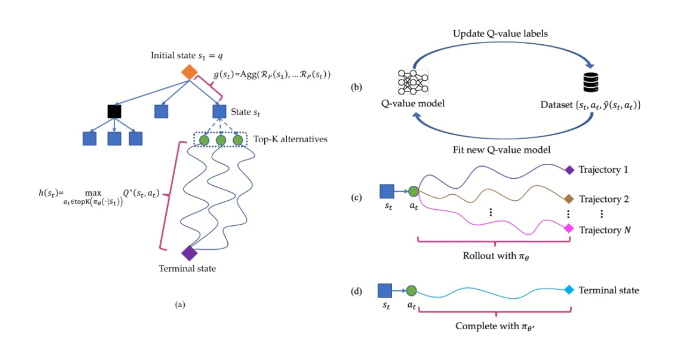
The Q* algorithm works by decomposing the reasoning trajectory of large language models into several states, planning each state comprehensively, and using the A* search algorithm to prioritize complex reasoning tasks. Additionally, they trained a proxy Q-value model through supervised learning to obtain the optimal Q-value for state-action pairs, thereby improving model performance.
Key Points:
🔍 The Q* project, not released by OpenAI, significantly enhances the reasoning capabilities of smaller models through the research team's algorithm.
🔍 The project has achieved notable experimental results on multiple datasets, demonstrating the potential and effectiveness of the Q* algorithm.
🔍 Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.14283









