At GTC2025, NVIDIA officially announced its next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) chip platform, named "Vera Rubin," honoring the renowned American astronomer Vera Rubin and continuing NVIDIA's tradition of naming architectures after scientists. The first product in this series, the Vera Rubin NVL144, is expected to be released in the second half of 2026.
NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang stated that Rubin's performance will reach 900 times that of the current Hopper architecture. In comparison, the latest Blackwell architecture already boasts a 68-fold performance improvement over Hopper, suggesting Rubin will bring another massive leap in computing power.

According to official information, the Vera Rubin NVL144 boasts an inference computing power of 3.6 ExaFLOPS in FP4 precision and a training performance of 1.2 ExaFLOPS in FP8 precision. Compared to the GB300NVL72, this represents a 3.3-fold performance improvement. Rubin will feature the latest HBM4 memory with an astounding 13 TB/s bandwidth and 75 TB of fast memory, 1.6 times that of its predecessor. In terms of interconnect, Rubin supports NVLink6 and CX9, with bandwidths of 260 TB/s and 28.8 TB/s respectively, both double that of the previous generation.
The standard version of the Rubin chip will be equipped with HBM4 memory, and its overall performance will significantly surpass the current flagship Hopper H100 chip.
It's worth mentioning that the Rubin platform will also introduce a new CPU called Veru, the successor to the Grace CPU. Veru contains 88 custom Arm cores, each supporting 176 threads, and achieves high-bandwidth connectivity up to 1.8 TB/s through NVLink-C2C. NVIDIA stated that the custom Vera CPU will be twice as fast as the CPU used in last year's Grace Blackwell chip.
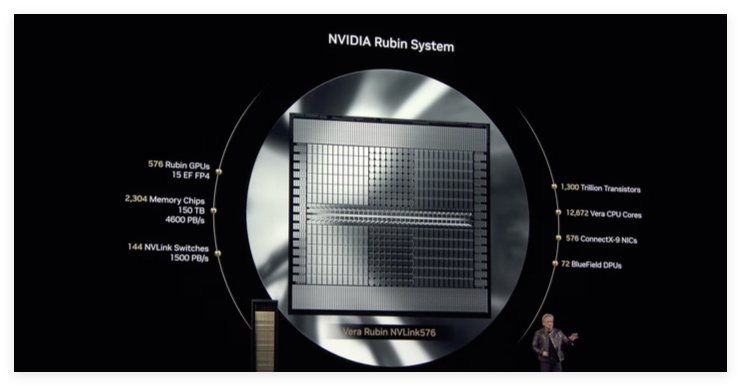
When used with the Vera CPU, Rubin's computing power in inference tasks can reach 50 petaflops, more than double the 20 petaflops of Blackwell. Furthermore, Rubin will support up to 288 GB of HBM4 memory, crucial for developers working with large AI models.
Similar to Blackwell, Rubin actually consists of two GPUs integrated into a single unit through advanced packaging technology, further enhancing overall computational efficiency and performance. The release of Rubin undoubtedly showcases NVIDIA's strong innovation in AI chips and its deep understanding of future computing power demands.